Angular I Core
Overview
- How to break your app into components
- How to make reusable components using inputs
- How to handle user interactions, such as clicking on a component
Model
Product Model
One of the key things to realize about Angular is that it doesn’t prescribe a particular model library.
Angular is flexible enough to support many different kinds of models (and data architectures). However, this means the choice is left to you as the user to determine how to implement these things.
1 | /** |
We’re creating a new Product class and the constructor takes 5 arguments. When we write public sku: string, we’re saying two things:
- there is a
publicvariable on instances of this class calledsku skuis of typestring.
If you’re already familiar with JavaScript, you can quickly catch up on some of the differences, including the
public constructorshorthand, here at learnxinyminutes
This Product class doesn’t have any dependencies on Angular, it’s just a model that we’ll use in our app.
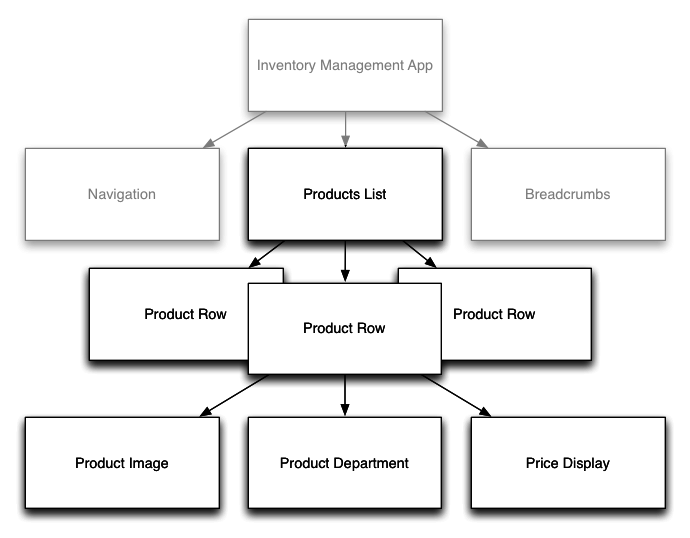
Components
Each component is composed of three parts:
- Component Decorator
- A View
- A Controller
Decorator
1 | @Component({ |
The @Component is called a decorator. It adds metadata to the class that follows it (AppComponent). The @Componentdecorator specifies:
- a
selector, which tells Angular what element to match - a
template, which defines the view
The Component controller is defined by a class, the AppComponent class, in this case.
Component => Services => API (Rest) HTTP Call Ajax Call in Angular HttpClient => API
Async/await and Tasks
Promises
Observiables =>
Observer pattern
Publish/subscribe pattern
